New tools to look at atomic nanoverse
 Australian researchers have gathered a set of advanced devices that will allow them to peer into the tiniest corners of the universe.
Australian researchers have gathered a set of advanced devices that will allow them to peer into the tiniest corners of the universe.
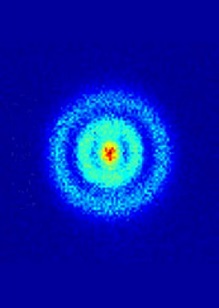
A team at the Monash Centre for Electron Microscopy (MCEM) has developed new methods which allow the very smallest displacement of atoms to be witnessed and measured.
New research, published in Nature Materials, provides immediate insights into lithium-ion battery performance and far-reaching implications for the design of new materials for energy generation and storage, next gen computing, green technologies, and other areas.
“The Monash research is like doctors being able to ‘see’ behaviours of individual viruses rather than just imagining them by observing the symptoms,” said lead research author Dr. Ye Zhu.
“We can study atomic behaviour with picometre precision. To put this in perspective, a hydrogen atom has an estimated diameter of [around] 50 picometres,”
By manipulating these atomic displacements, researchers have the potential to create ‘wonder materials’ for use in applications such as high performance computers, ultra-efficient solar cells and environmentally friendly sensors.
“Atoms are the building blocks of nature. If the position of these building blocks is varied, even slightly, the impact on the function of a material can be profound,” said corresponding author Professor Joanne Etheridge.
“This new method, combined with MCEM’s powerful electron microscopes, has unveiled exquisitely subtle variations in the arrangement of atoms that drive the important properties of this material.”
Researchers believe that the imaging method should be equally applicable to a variety of material systems and will become a popular and powerful tool in providing real-space structure information.
“This paper reveals the extraordinary power of modern electron microscopy to directly map the fine details of complex crystal structure, in this case that of a remarkable self-assembled nanostructure with a compositionally tuneable nano-scale periodicity,” co-author Professor Ray Withers of ANU said.
The MCEM is a leading research centre in electron microscopy that combines a state-of-the-art technology with international specialist expertise in the development of methods to determine atomic structures.







 Print
Print